NEXT-GENERATION SENSORS
Radar
CPRR24
FMCW continuous-beam radar with progressive digital beam forming and MIMO technology, providing the best angular resolution in its class*
* Based on the analysis of the characteristics of radar sensors of similar purpose
Cognitive Imaging 4D Radar
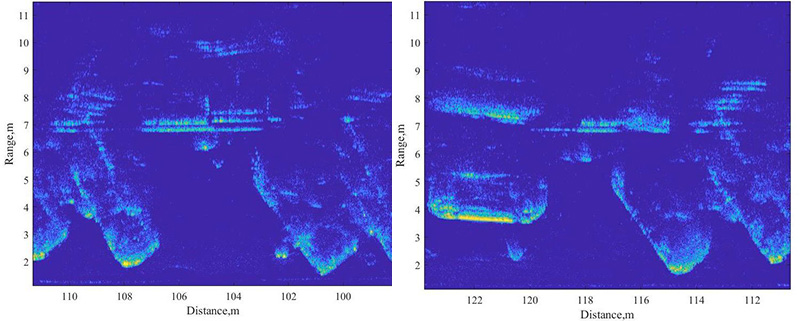
Unlike conventional radar systems, Cognitive Imaging Radar determines not only the coordinates and the velocity of road scene objects but also their shape and type. The information supplied by the system produces a detection accuracy of up to 97.7% and, in combination with a video camera, ensures safety on the road.
Cognitive Imaging Radar can detect objects at a distance of up to 280–300 m and within an azimuth angle of over 90˚–100˚ and an elevation angle of up to 15˚–20˚ (expanding this range serves no practical purpose). Its working frequency is within the range of 76–81 GHz.
A conventional radar unit performs a scan of the surroundings in a single plane, while Cognitive Imaging Radar scans space in every possible direction.
Regular radar can determine the distance to objects in a road scene, their trajectory and velocity. It is not capable of determining the shape or type of objects. For example, it is practically incapable of distinguishing between a car and a pedestrian or an approaching bridge and a heavy truck. Neither can it process overlapping images, such as a pedestrian standing in front of a fence or a car.

The video demonstrates the functional difference between Cognitive Imaging 4D Radar and lidar in cloudy and dusty conditions.
Cognitive Imaging Radar employs the SAR (Synthetic-Aperture Radar) technology, which recreates the surroundings by producing a map based on data from the radar and the vehicle’s onboard computer. The autopilot uses this map to understand the general position of the car and the possible scenarios of motion path selection. The technology ensures that objects located close to the vehicle – such as the road shoulder, potholes, curbs, and so on – can be seen in high-quality resolution. This was a known issue for previous-generation radar and 4D-radar projects developed in other countries. It can also see and detect even pets, identify potentially hazardous road objects, and take them into account when operating a driverless car.