URBAN TRANSPORT
AI-based tram driving assistance system



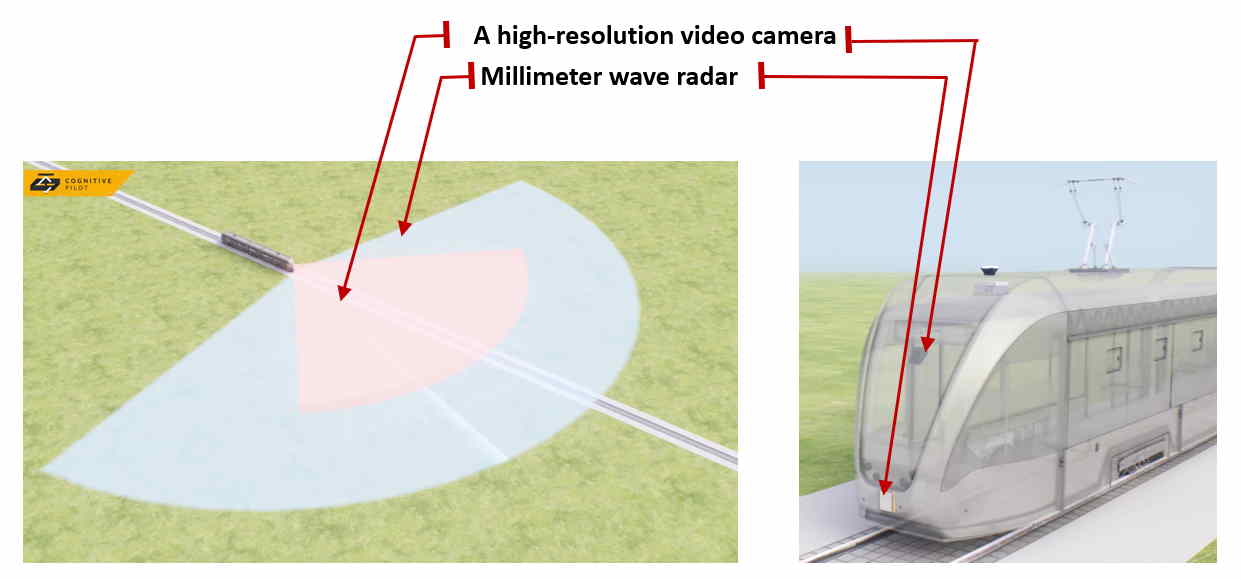
- Video camera unit with an electronic climate control and maintenance system and a three-axis vibration dampener
- Specialized high-resolution millimeter wave radar
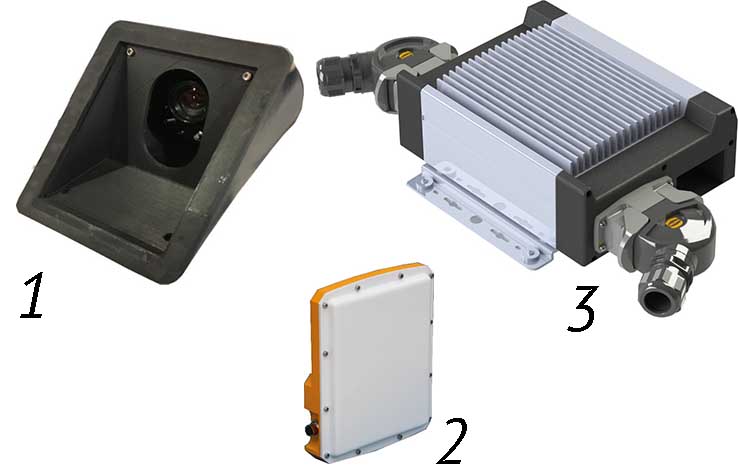

- High-performance industrial-grade computing unit
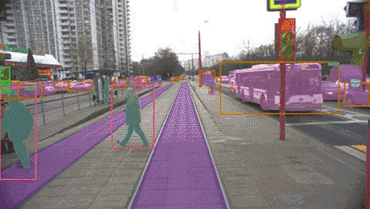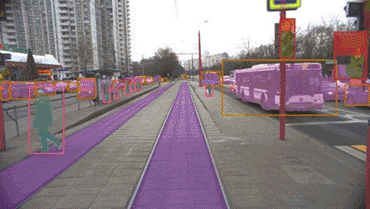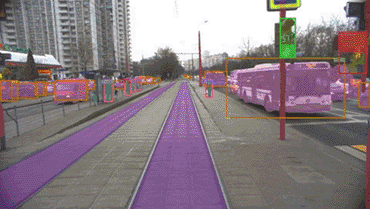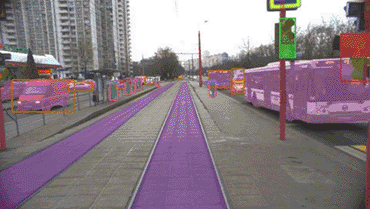
How Cognitive Tram Pilot recognizes objects ahead
Our original deep learning neural networks and post-processing algorithms…
 1
1
 2
2
 3
3
The Cognitive Tram Pilot hardware and software suite includes a machine vision system and a set of sensors that depends on the specific task, type of car, and other factors. It can include from 10 to 20 video cameras located along the outside of the tram (for long, three-unit trams) and up to 10 radar units. There is also an option to install onboard GPS sensors. While in motion, the system employs high-accuracy mapping.
In 2019, Russia’s leading tram manufacturer PC “Transport systems” and Cognitive Pilot announced a joint project to design an autonomous tram for the domestic and foreign markets. Moscow is one of the few cities in the world which is continuously improving its transportation network and making use of cutting-edge technologies in the transport industry.
In the first stage of its deployment, the Cognitive Tram Pilot intellectual driving system will perform the functions of an active assistant in dangerous situations should the driver fail to react properly.
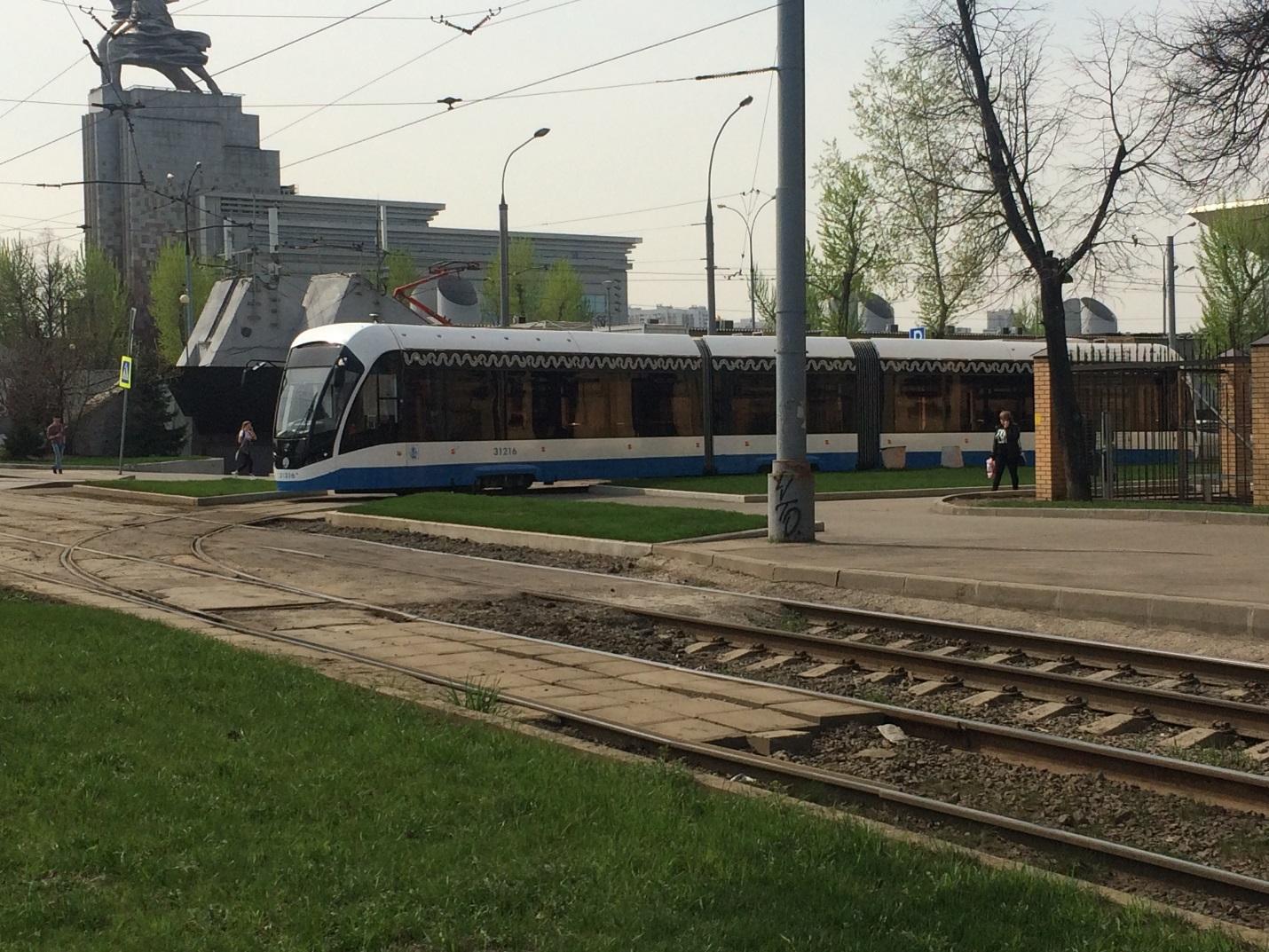
PC Transport Systems is currently carrying out joint tests with Cognitive Pilot on public roads to enhance active safety and optimize the tram service. Tram route #17 (Ostankino – Medvedkovo) has been selected as the pilot route for testing. The tests are being performed on a Vityaz–M, a modern, innovative tram car manufactured by PC Transport Systems and used by Mosgortrans, Moscow’s public transport operator.
During the tests, the driver is present in the cab at all times and controls safety along with performing other tasks. Experts from the two companies have been focusing on testing systems such as the automated braking system, which enhances safety when the tram is in motion by assisting the driver in the detection of obstacles on the road, and speed control, which enables the test tram to maintain an appropriate speed and identify high-risk sections of the route with the highest possible efficiency.



